The Art of Predynastic Egypt Is Principally Made of Quizlet
Due eastgyptian fine art is widely considered to be 1 of the nearly striking fine art forms to ever exist. The well-nigh well-known examples of Egyptian fine art that have survived to this day were produced between the 31st century B.C. and the ivth century A.D. Despite seeming blowsy, equally fine art is no longer produced in the same style, ancient Egyptian art remains a fascinating genre to learn virtually, as the purpose of fine art then differed profoundly in comparison to what fine art stands for today.
Tabular array of Contents
- one Why Was Egyptian Art And so Of import?
- 2 What Did Ancient Egyptian Art Correspond?
- 2.1 Affectionate and Understanding Ancient Egyptian Art
- two.2 Art Not Meant for Public Viewing
- two.three The Use of Text and Image
- ii.4 The Importance of Scale
- ii.five The Function of Egyptian Art
- 2.6 The Touch on of 2-Dimensional Art
- 2.7 The Impact of Three-Dimensional Art
- 3 The Chronology of Egyptian Art
- 3.i Pre-Dynastic Egyptian Art (6000 – 3000 B.C.)
- three.2 Early Dynastic Egyptian Fine art (c. 3150 – 2686 B.C.)
- iv Characteristics of Egyptian Fine art
- 4.one Anonymity in Egyptian Art
- iv.2 Symbolism in Egyptian Art
- iv.3 Symmetry in Egyptian Art
- 5 Types of Egyptian Art
- 5.1 Egyptian Paintings
- 5.2 Egyptian Drawings
- v.3 Egyptian Sculpture
- half dozen Iconic Egyptian Artwork
- 6.ane The Groovy Pyramids of Giza
- 6.ii Pyramid of Khufu
- 6.3 Pyramid of Khafre
- 6.4 Pyramid of Menkaure
- 6.5 The Peachy Sphinx
- 6.half dozen Tutankhamun's Tomb
- 7 Influence and Legacy of Egyptian Fine art
- 8 Frequently Asked Questions About Egyptian Fine art
- 8.1 What Is Egyptian Art?
- 8.two What Were the Important Characteristics of Egyptian Art?
- 8.3 What Are Some of the Most Famous Examples of Egyptian Fine art?
Why Was Egyptian Fine art So Important?
The artworks that take come from ancient Egypt take been a topic of great captivation and obsession for people for thousands of years. This is partly due to the techniques of Egyptian art having inspired both Greek and Roman artists who were influenced by the remarkable sculptures, paintings, drawings, jewelry, and architectural structures that were made.
It has been said that even artworks of certain cultures existing in the present twenty-four hour period have been swayed past the talents of Egyptian art, demonstrating its worldwide bear upon.
Every bit very petty outside influence was able to sway the characteristics of Egyptian fine art, most of the artworks that were made remained exceptionally stable during the genre'due south most 3000-year catamenia. The anonymity associated with artists was an of import element within the production of ancient Egyptian art, as nigh of them remain unknown to this day. This was due to the fact that art was more functional as opposed to aesthetic, every bit information technology was substantially created for a applied purpose.
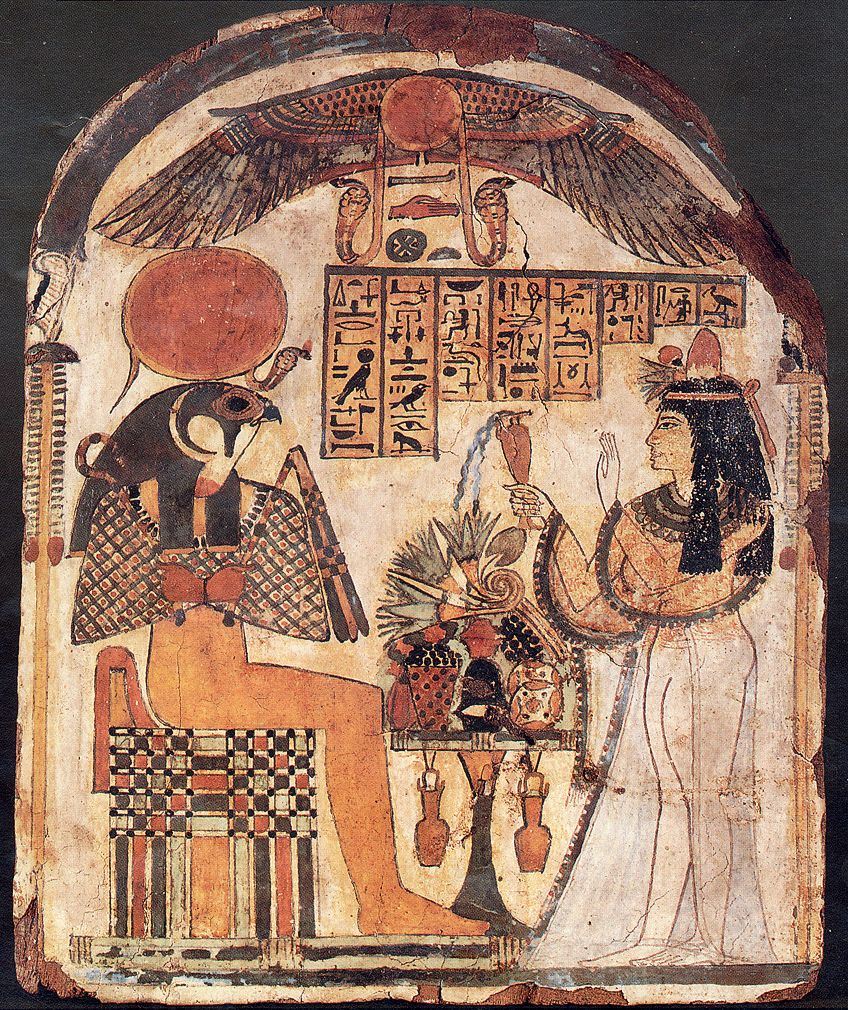 Ancient Egyptian wooden stela depicting Lady Djedkhonsuiwesankh giving offerings of food, beverage, and flowers to Re-Horakhty (c. 950–700 BC);Photograph by Oriental Institute, the University of Chicago; painter unknown, Public domain, via Wikimedia Eatables
Ancient Egyptian wooden stela depicting Lady Djedkhonsuiwesankh giving offerings of food, beverage, and flowers to Re-Horakhty (c. 950–700 BC);Photograph by Oriental Institute, the University of Chicago; painter unknown, Public domain, via Wikimedia Eatables
While more artists from the later periods of Egyptian art are known by name, the artworks that notwithstanding hold the greatest attractions are those that were fabricated centuries ago by unidentified creatives. This chemical element of curiosity has also added to the great intrigue plaguing ancient Egyptian fine art for and then long, every bit the artworks differ greatly from the type of art that is typically produced today.
In order to recognize the significance of Egyptian art, it is important to view the artworks from the perspective of the ancient Egyptians themselves.
Despite all of the numerous exhibitions that have featured Egyptian art throughout the years, the artists of the work would never have understood the relevance of placing their work completely out of context in a museum. This was because art was traditionally made to beautify tombs and was typically reserved for the wealthy who could afford to committee such pieces.
Equally time went on, ancient Egyptian art reached a substantial level of elegance, with the tombs, temples, tomb paintings, sculptures, and inscriptions becoming very stylized and symbolic. This was to emphasize the fact that ancient art served a primarily useful purpose, such as tomb art that represented scenes from one's life on world and so that one'southward spirit would be able to call back it. Due to this, the majority of Egyptian history and civilization has come up to exist known through the artworks that take been institute, which further indicates their importance.
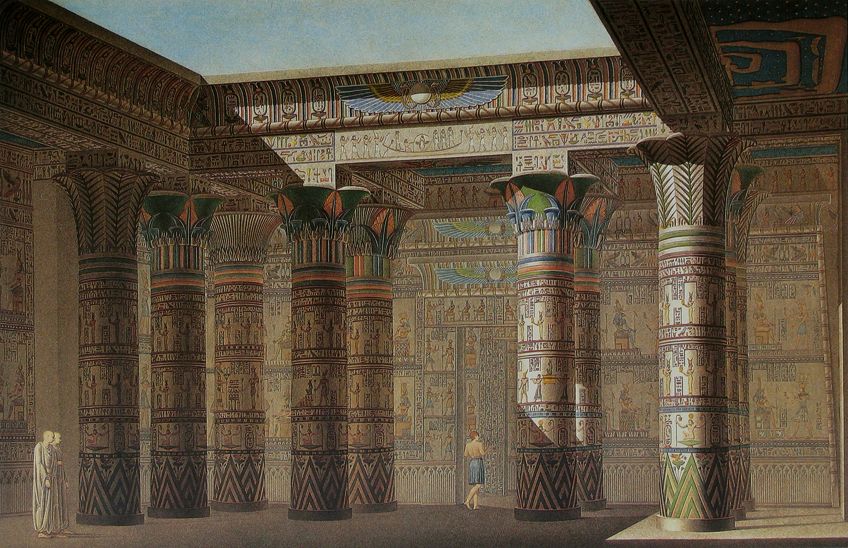 Inside the Temple of Philae in Egypt, picture from the Clarification De Fifty'Egypte(1821/1822);Jean-Baptiste Lepère, Allais, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Inside the Temple of Philae in Egypt, picture from the Clarification De Fifty'Egypte(1821/1822);Jean-Baptiste Lepère, Allais, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
However, equally only the aristocracy could afford such art, the pieces that take been found are mostly concerned with the lives of the upper form. It is simply through understanding these pieces and stories that those of the lower classes have been exposed, which demonstrated the complexity of ancient Egyptian art.
Every bit nigh of the remaining art that exists today has been constitute in tombs and monuments, greater attention on life after expiry and the conservation of prior information can be seen. Thus, agreement the importance of Egyptian art lies in appreciating what the artworks were actually created for, equally they served a vastly unlike purpose when compared to the types of art that exist today.
What Did Aboriginal Egyptian Art Represent?
Within any blazon of culture, art has been seen as a fundamental attribute throughout the centuries. Arab republic of egypt is no unlike, with the introduction of artworks existence traced back to the Predynastic Menstruation between 6000 and 3150 B.C.E. Images of animals, humans, and mystical figures have been found etched onto rock walls, which represents the estimated origin of art within aboriginal Egypt. While these depictions are seen equally unrefined in comparison to the subsequent developments of art, they all limited the of import Egyptian value of residuum.
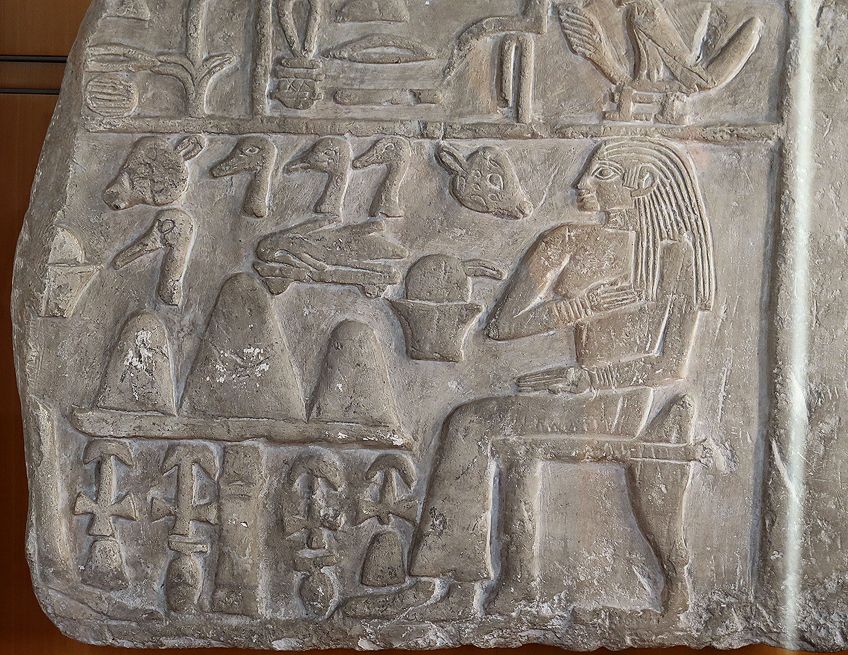 Fragment of a stele in the proper name of Nes-Henou, from the Thinite flow, 2nd dynasty (2925-2700 BCE); Ismoon (talk) 19:09, 27 July 2020 (UTC), CC By-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Fragment of a stele in the proper name of Nes-Henou, from the Thinite flow, 2nd dynasty (2925-2700 BCE); Ismoon (talk) 19:09, 27 July 2020 (UTC), CC By-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Starting from the Early Dynastic Period until Roman Arab republic of egypt when Christianity came in, the blazon of Egypt fine art included ivory sculptures, paintings, papyrus drawings, faience, and jewelry. Additionally, architecture was experimented with, which can exist seen in the iconic pyramids and temples that Egypt is typically known for. Despite so much time passing between the introduction of ancient Egyptian fine art, the style has remained quite bourgeois and has changed relatively little in comparison to other art forms.
The majority of the surviving fine art that is known about and on brandish today has come from the earthworks of certain tombs and monuments.
Through this, social club has been given more information and understanding into the afterlife principles that were held by the aboriginal Egyptians. For example, the charms and amulets found in these sites were said to protect the deceased from danger, while the figurines protected them from evil spirits and angry ghosts.
Additionally, the tomb paintings were said to depict scenes from the paradise that those wished to find in the afterlife, with the paintings existing as a type of map to aid the departed discover their way. Based on this, we can understand why the artworks produced past the ancient Egyptians served a function as opposed to only beingness viewed. Every bit Egyptian artwork was primarily bound in religion and ideology, artists portrayed a very idyllic and unrealistic view of the world as no specific creative expression existed since art served a wider purpose.
 Nakht and Family unit Line-fishing and Fowling, Tomb of Nakht (circa 1400 –1390 B.C.);Metropolitan Museum of Art, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
Nakht and Family unit Line-fishing and Fowling, Tomb of Nakht (circa 1400 –1390 B.C.);Metropolitan Museum of Art, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
As an art form, artful beauty was non the incentive behind the creation of most Egyptian artwork. At the time, Egyptian society was based on the notion of harmony, also known as "ma'at". This led to Egyptian art being created in perfect balance because it reflected the platonic earth of gods.
No matter how beautifully an artwork was crafted, its purpose to serve as a home for a spirit or god was of the utmost importance. Their function was to exist as a reminder of the everlasting nature of life and the value of personal and collective stability.
Appreciating and Understanding Ancient Egyptian Art
In order to truly understand the purpose of ancient Egyptian art, the artworks need to exist looked at from the perspective of the Egyptians who produced them. This was because the art of the Egyptians served a significantly different intention to the fine art of later cultures and today, every bit traditional Egyptian art prioritized function over form. This led to the cosmos of artworks that were quite stable and conventional in blueprint but were also unusually abstract and stocky. Due to this, unflattering comparisons to later styles of Greek and Renaissance art were made, as these artworks were more naturalistic in nature.
The comparisons fabricated demonstrated the uniquely different properties that Egyptian art subscribed to when assorted against other forms of art, which indicated the importance of understanding the aim of Egyptian artwork.
Art Non Meant for Public Viewing
While the artworks that are produced today are more often than not made to be viewed by an audience, aboriginal Egyptian art differed greatly in this regard. Despite the world marveling at the dazzling treasures found in the tomb of Tutankhamun and the breathtaking reliefs within the New Kingdom tombs, it is of import to remember that ancient Egyptian art was never intended to be seen by others. These artworks were solely made for the deceased, every bit their only purpose was to guide the spirit in the afterlife and decorate the tomb.
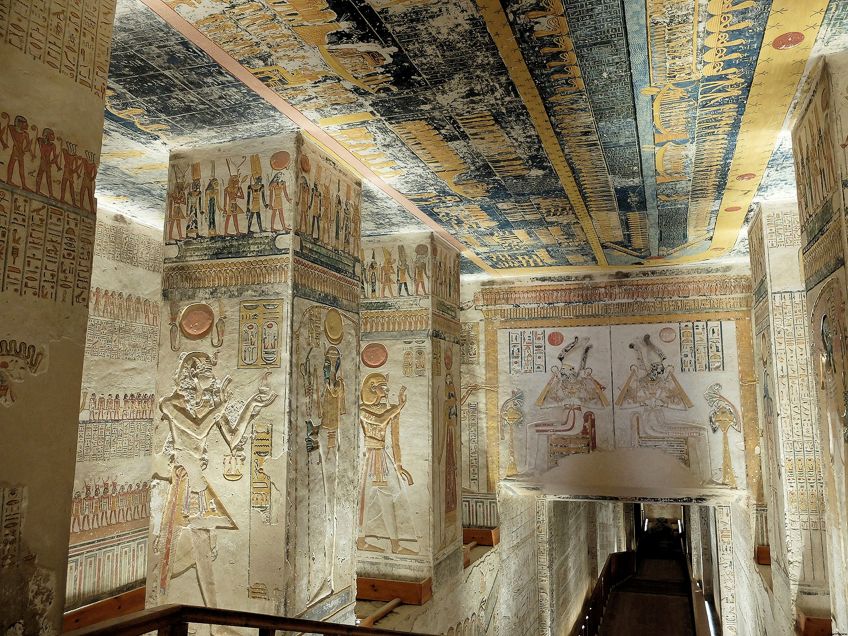 KV9, Tomb of Ramses V-VI. Pillared hall, left side;R Prazeres, CC By-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
KV9, Tomb of Ramses V-VI. Pillared hall, left side;R Prazeres, CC By-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
The Use of Text and Image
A feature that is quite remarkable about Egyptian art is that text was fastened to near all of the images produced. This is nearly notably seen in the statues and relief paintings created, equally hieroglyphics were attached to these works. On the statues, identifying and explanatory text ordinarily appeared on the dorsum pillar or base of operations that supported the work, while relief paintings and panels tended to have longer captions that explained and completed the stories in the scenes.
 An Egyptian hieroglyphic detail of the Stele of Minnakht, master of priests at Akhmim. At that place are iv lines of hieroglyphs: Line 1 depicts a Shen loop, spit of land, 3 strokes, a man, arms in negation, an incense bowl, and an Ibis bird. Line 2 depicts a f ield of reeds, a plinth shape, plants, and a jug with a handle. Line 3 depicts H-Ra-H 'block', a fence, meat, and crossed strokes. Line 4 depicts an eye, water jug, a face, and an arm with conical breadstuff;Guillaume Blanchard, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
An Egyptian hieroglyphic detail of the Stele of Minnakht, master of priests at Akhmim. At that place are iv lines of hieroglyphs: Line 1 depicts a Shen loop, spit of land, 3 strokes, a man, arms in negation, an incense bowl, and an Ibis bird. Line 2 depicts a f ield of reeds, a plinth shape, plants, and a jug with a handle. Line 3 depicts H-Ra-H 'block', a fence, meat, and crossed strokes. Line 4 depicts an eye, water jug, a face, and an arm with conical breadstuff;Guillaume Blanchard, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Hieroglyphs were also seen as artworks in and of themselves, despite these pocket-sized inscriptions non e'er continuing for what they depicted. Traditionally, hieroglyphs were phonetic sounds that were used to explain the images they were continued to. Even so, they were sometimes logographic in nature, every bit they represented the actual object and concept in word form.
Despite this, a fine line existed between text and images in many cases.
This was because the proper name of a figure in the text of the statue frequently left out the determinative, which was an implicit sign that aided in identification. For case, all verbs of motility were unremarkably followed by a pair of walking legs to further demonstrate the meaning of the hieroglyph.
The Importance of Scale
In order to accurately convey hierarchy within ancient Egyptian artworks, differences in scale stood out as the nigh normally used method. Through this utilise of deviation, one could assume that the larger the scale of the figure, the more than important that specific individual was. As a result of this, kings were most commonly shown to be the aforementioned calibration as deities, as both figures were traditionally depicted as larger and more aristocracy than common Egyptian individuals.
 Queen Nefertari being led by Isis, the daughter of the earth god Geb and the sky goddess Nut (circa 1279 –1213 B.C.);Metropolitan Museum of Art, CC0, via Wikimedia Eatables
Queen Nefertari being led by Isis, the daughter of the earth god Geb and the sky goddess Nut (circa 1279 –1213 B.C.);Metropolitan Museum of Art, CC0, via Wikimedia Eatables
The Function of Egyptian Art
No matter what type of artworks were produced, such as statues or relief paintings, they were all intended for the aforementioned purpose. All artworks were essentially created to serve in the interest of a heavenly or departed recipient, every bit they provided a place for the individual to manifest and receive the full benefits of ritual actions.
For example, the majority of statues demonstrated a formal frontality. This meant that they were organized directly ahead so as to directly face the ritual of saying cheerio to a loved one that happened right in front of them.
No matter if statues were holy, imperial, or aristocracy, they all worked to provide a blazon of channel for the spirit of the deceased that allowed them to interact with the temporal world. These statues were seen as mediators that existed between the worlds of the people and the gods, which enabled a form of communication to take place and so that both sides were never forgotten.
The Impact of Two-Dimensional Art
Ancient Egyptian art made use of both two-dimensionality too as iii-dimensionality in the artworks that were created. As both forms differed profoundly, two-dimensional art was said to nowadays the most representative aspects of each component in the scenes as opposed to creating artworks that merely replicated the physical world. In order to create these dazzling two-dimensional artworks, each element within a scene was depicted from its most distinguishable bending and so afterward grouped together in social club to brand the whole.
This was why the angles of humans appeared strange, equally the face, waist, and limbs were typically shown in profile while the eye and shoulders were represented frontally. Despite being seen every bit quite complicated, two-dimensional depictions provided consummate information almost the unlike elements included to create a very comprehensive image.
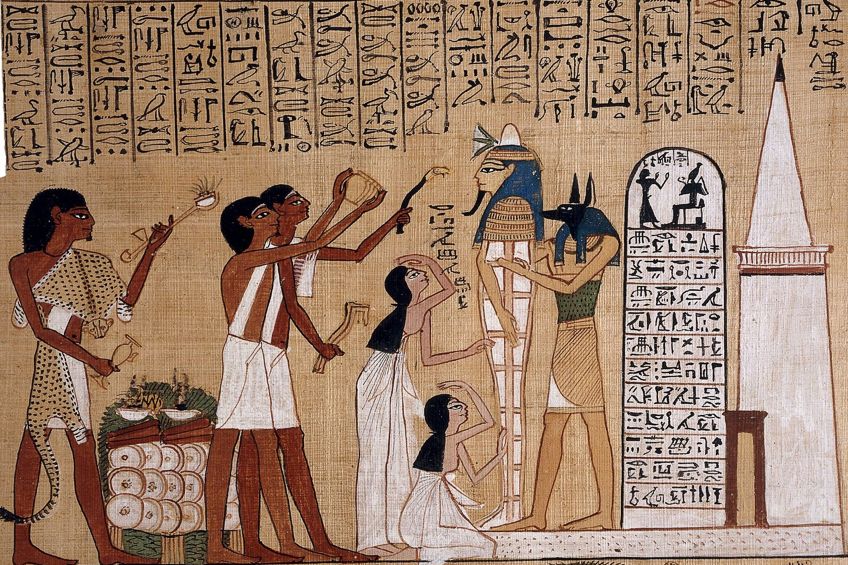 Ancient Egyptian Papyrus from the Volume of the Dead of Hunefer, depicting the "opening of the mouth" ceremony (1275 B.C.). A more detailed explanation of the scene can be found in the public domain The Book of the Expressionless, by E. A. Wallis Budge;Hunefer, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Ancient Egyptian Papyrus from the Volume of the Dead of Hunefer, depicting the "opening of the mouth" ceremony (1275 B.C.). A more detailed explanation of the scene can be found in the public domain The Book of the Expressionless, by E. A. Wallis Budge;Hunefer, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
The Impact of Three-Dimensional Art
In comparing, three-dimensional art worked to produce the well-nigh lifelike and realistic depiction of the existent world as possible. Due to this, these artworks were seen equally very formal in nature, as statues of the gods, royalty, and the elite was designed to project an idealized and romanticized version of that private. Aspects of naturalism were also seen, yet this depended on the type of fabric used as dissimilar materials were able to lend themselves in various ways to certain positions.
For example, rock statues appeared to be very closed-off and tight, as the artillery of the figures were typically shown to exist held close to their sides. This represented their limited room, equally the merely bits of space that were seen were in between the areas left open between the dorsum supporting colonnade and the figure'due south limbs.
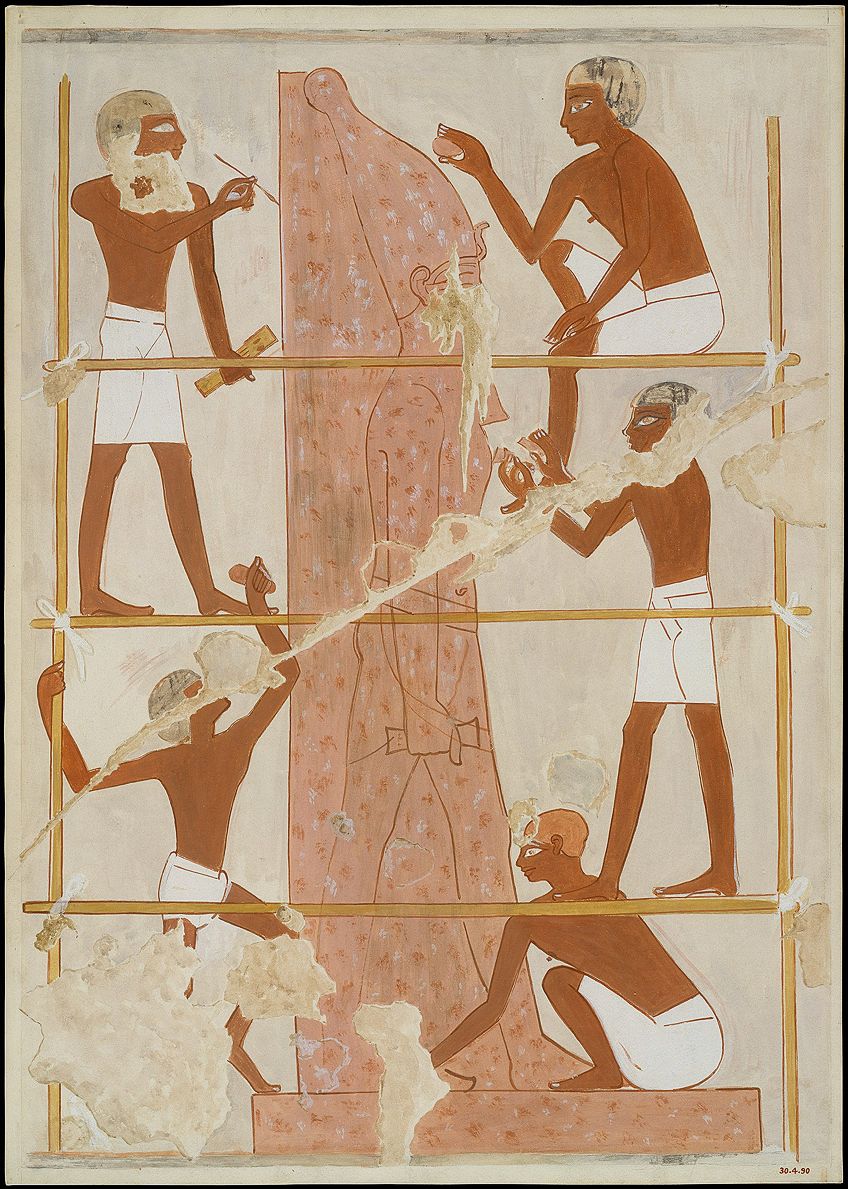 Sculptors at Work, Tomb of Rekhmire (circa 1479 –1425 B.C.);Nina M. Davies, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
Sculptors at Work, Tomb of Rekhmire (circa 1479 –1425 B.C.);Nina M. Davies, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
By contrast, wood and metal statues were more expressive, as the arms of statues were able to be extended and fully opened up. Additionally, these statues had more than spaces between their limbs and were even found to be holding few objects too, which gave them a more than realistic appearance.
Despite the different materials used, all iii-dimensional statues served the aforementioned purposes and maintained an identical type of formalization and frontality.
The Chronology of Egyptian Art
The artworks produced in Arab republic of egypt have an incredibly long history, equally the majority of the pieces date back thousands of years agone. Due to this, the two full general periods that Egyptian artwork has been classified into are the pre-dynastic Egyptian art menses and the early dynastic Egyptian art menstruum. Below, we will be taking a look at the unlike types of art genres and cultures that made up each flow.
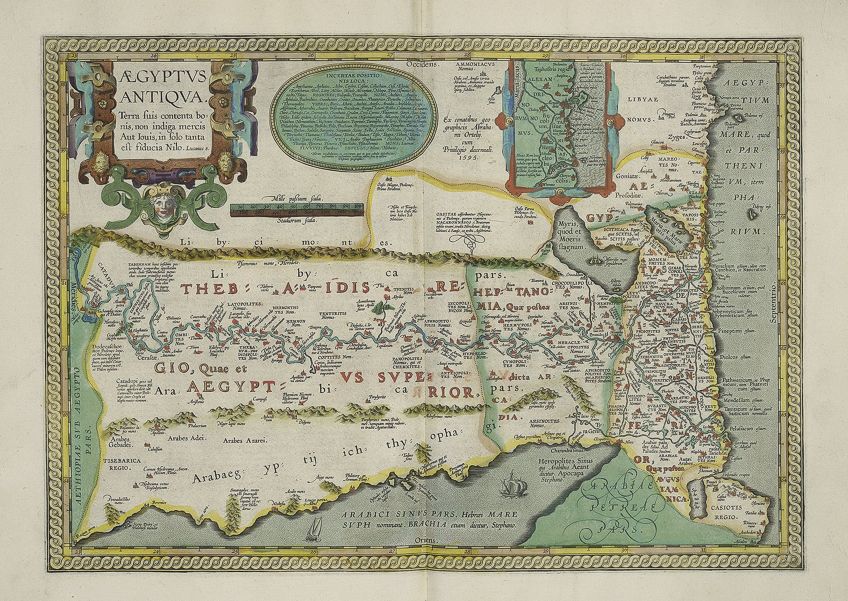 Map of ancient Egypt and inset map of the area effectually Alexandria by Abraham Ortelius, c. 1608; Folger Shakespeare Library, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Map of ancient Egypt and inset map of the area effectually Alexandria by Abraham Ortelius, c. 1608; Folger Shakespeare Library, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Pre-Dynastic Egyptian Art (6000 – 3000 B.C.)
Spanning for approximately 3000 years, the pre-dynastic Egyptian art menses was fabricated up of three dominant cultural eras: the Merimde civilisation, the Badarian culture, and the Naqada culture. Often compared to the Neolithic period of art, pre-dynastic Egyptian fine art was named afterwards the various areas where certain types of Egyptian settlements were discovered.
Every bit Egyptians began to settle along the Nile river and adopt more of an inactive lifestyle during the Neolithic period, very little archeological evidence has been constitute for the years preceding 6000 B.C. However, as Arab republic of egypt entered into the pre-dynastic era, more settlements began to appear, which accounted for the vast majority of the pre-dynastic archeological artworks that were plant within Upper Egypt.
Early Dynastic Egyptian Fine art (c. 3150 – 2686 B.C.)
Equally more artworks appointment back to the early dynastic menses, more information is known about this artistic era in Egypt. Emerging afterward the amalgamation of Lower and Upper Egypt around 3100 B.C., the early dynastic catamenia is mostly included as role of the Commencement and 2nd Dynasties, which lasted until the start of the Old Kingdom during 2700 B.C.
At this point in Egyptian art, the defining characteristics of all aboriginal Egyptian civilizations, including art, architecture, and faith, began to take form during this period.
The majority of Egyptian art within this period revolved around the themes of permanence and preservation, every bit artists attempted to safeguard and conserve everything in equally much of a fixed fashion as possible. This led artists to produce sculptures and relief paintings that portrayed gods, humans, mettlesome battles, and nature, as these were meant to provide some form of comfort to the deceased in the afterlife.
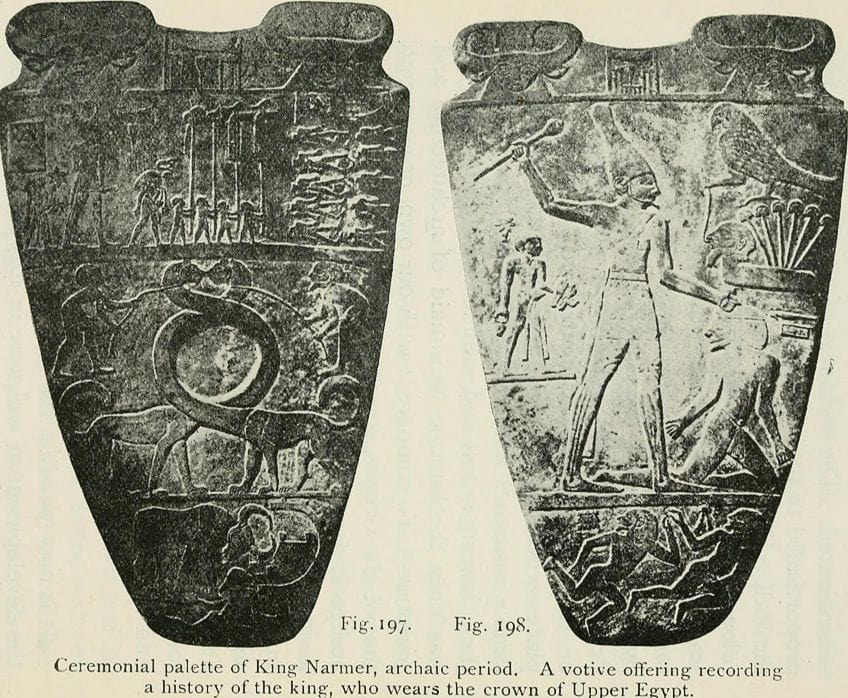 The Narmer Palette, belonging to King Narmer in the archaic catamenia. A votive offering recording a history of the kind, who wears the crown of Upper Arab republic of egypt; Internet Archive Volume Images, No restrictions, via Wikimedia Commons
The Narmer Palette, belonging to King Narmer in the archaic catamenia. A votive offering recording a history of the kind, who wears the crown of Upper Arab republic of egypt; Internet Archive Volume Images, No restrictions, via Wikimedia Commons
The common artful practices of symbolism, residue, and symmetry that were all used to create the iconic Egyptian artworks renowned today were formalized during the early on dynastic menstruum. These values infused Egyptian paintings and sculptures from the earliest periods of art, with rock art existing as a good example of this.
During the pre-dynastic menses, rock art emerged but was non actually understood according to the ascendant artistic elements, until it was fully realized in the early dynastic menses.
Artworks from the early on dynastic menstruum reached their peak in an archeological sculpture that was known as The Narmer Palette, dating between 3200 and 3000 B.C.E. This artwork clearly demonstrated and celebrated the unity between Upper and Lower Egypt under King Narmer's dominion. The engravings on the slab told the story of King Narmer'due south victory over his enemies and how the gods supported his deportment.
Characteristics of Egyptian Art
Throughout history, Egypt art has typically been known for its unique effigy convention that has been used to depict the main figures seen in both relief sculptures and paintings. Egyptian art has made meticulous use of hierarchical proportions which accept gone on to narrate and identify their works as important pieces of art. This has also aided in the farther understanding of ancient Egyptian artworks, as certain attributes be as significant features that define and prepare their works apart from others.

An analogy by Giovanni Battista Belzoni (1778-1823) of Plates reminiscent of the researches and operations taking place in Egypt and Nubia. The upper role represents the Eagle analogy from the king's tombs in Thebes;Costless Public Domain Illustrations by rawpixel, CC BY two.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Anonymity in Egyptian Art
Ane of the most prominent features of Egyptian art is that artists rarely put their names on the artworks they created. Due to this, the majority of the artists who created works during the dissimilar creative and cultural eras of Egypt remain unknown to this day. This was mainly due to the fact that artists viewed art as serving a functional purpose equally opposed to an aesthetic 1, then knowing who created an artwork was seen every bit irrelevant by Egyptian society.
Additionally, Egyptian artwork remained mostly anonymous because it was essentially collective, as only the families who commissioned the works were able to view them.
By removing the names of artists from their works, the notion of status was taken away completely. Importance through art was only given to the gods and the divine pharaoh's through their statuary depictions, every bit they were typically scaled to exist larger than other figures to demonstrate their dominance and authority.
Symbolism in Egyptian Fine art
Within ancient Egyptian fine art, symbolism infiltrated almost every artwork that was made and went on to play a significant role in the establishment of society and sense. Every attribute of Egyptian art, no matter if they were sculptures designed for tombs or simple yet ornate hand mirrors and cosmetic cases for everyday use, was steeped in symbolic meaning. The wealthy of Egypt had the virtually access to these symbolic objects and artworks, every bit their existence depended on the material and fiscal resource bachelor to brand and pay for them.
 P apyrus of Hunefer, depicting the judgment of the dead in the presence of Osiris (circa 1275 BCE). A more detailed caption of the scene tin be found in the public domain The Volume of the Dead, past East. A. Wallis Budge;Hunefer, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
P apyrus of Hunefer, depicting the judgment of the dead in the presence of Osiris (circa 1275 BCE). A more detailed caption of the scene tin be found in the public domain The Volume of the Dead, past East. A. Wallis Budge;Hunefer, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
The about important artworks that were infused with heavy symbolism were depictions of the pharaoh's regalia. The purpose of depicting imperial attire in this style was to represent and emphasize the bully ability of the pharaoh and so that social club was able to exist maintained within Egyptian society.
In add-on to pharaohs and their attire, goddesses, gods, and animals were likewise represented as highly symbolic figures in Egyptian art, every bit they were regarded every bit ubiquitous and almighty figures.
Color also served a symbolic purpose, as they tended to be very expressive. The ancient Egyptian language divided color up into four bones groups, namely black, white/silvery, green/blue, and carmine/orangish/yellow, with each colour symbolizing a different meaning and concept. Typically, colour was used to advise themes relating to youth, royalty, and divinity within various artworks.
 Fragments of a sarcophagus with the deceased offerer at Anubis, III intermediate period-XXI dynasty;Sailko, CC Past 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Fragments of a sarcophagus with the deceased offerer at Anubis, III intermediate period-XXI dynasty;Sailko, CC Past 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Blueish was said to symbolize fertility and birth, with the blue and green tones existence seen as the colors of vegetation and renewal. Blackness was traditionally used to depict regal figures only, as it symbolized the fertile soil of the Nile from which Arab republic of egypt arose and was besides said to be associated with the afterlife and certain deities. Gilt was a unique color, as it symbolized divinity due to its uncommon advent and its connection to valuable materials and was regarded by Egyptians as "the flesh of the god".
While virtually colors appeared to have certain symbolism, carmine, orange, and yellowish were regarded as very fluctuating colors. They tended to exist linked to images of the sun, with carmine being used as the color of the desert, in certain gemstones that were used for royal statues, and to write important names on documents.
Symmetry in Egyptian Art
Symmetry was the tertiary characteristic that was considered to be important inside ancient Egyptian art. While these artworks were primarily motivated by the applied goal of functionality, all works needed to exist aesthetically cute likewise. Due to this, Egyptian art is constantly praised for its great beauty, which is all thanks to the value that ancient Egyptians placed on the characteristic of symmetry.
The search for perfect residue and symmetry inside ancient Egyptian fine art reflected the cultural value of harmony, which was a central notion to Egyptian culture at the fourth dimension.
In addition to being seen as a widespread notion at the time, symmetry was an ideal that came into being when the gods first ordered the universe. Symmetry was able to bring nearly the concept of unity and duality, which was represented through artworks that depicted both males and female person figures.
 Relief of Akhenaton and Nefertiti seated, property three of their daughters, nether the rays of the sun god Aton giving Ankh-symbols to them (ca. 1350-1340 B.C.); ArchaiOptix, CC Past-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Relief of Akhenaton and Nefertiti seated, property three of their daughters, nether the rays of the sun god Aton giving Ankh-symbols to them (ca. 1350-1340 B.C.); ArchaiOptix, CC Past-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
This concept of duality was essentially regulated by this harmony, with all Egyptian artworks, temples, homes, palaces, and gardens being created with balance in mind in order to reflect the value of symmetry. Egyptians believed that their land was made in the paradigm of the world of the gods and that when someone passed away, they would return to an afterlife and paradise that was somewhat familiar.
Thus, all art and architectural objects were intentionally laid out to express the perfect harmony that the gods began at creation.
Types of Egyptian Fine art
All artworks created within ancient Egypt were done to reflect the perfection of the gods, deities, and pharaohs at the time. In improver to existing as beautiful works of art, these artworks served a applied purpose on a daily basis. The most common types of Egyptian art that came from this era of history were Egyptian paintings, drawings, and sculptures, which nosotros will be discussing below.
Egyptian Paintings
The majority of the surviving paintings to come up from Arab republic of egypt were produced during the early dynastic period, hence the potent emphasis on life afterwards death that is seen. Great preservation of past knowledge is depicted in all of the ancient Egyptian artworks, with these paintings surviving thousands of years thanks to Egypt'due south incredibly dry climate. Another reason that Egyptian paintings accept been so durable is that many of them were designed to decorate the inside of tombs, meaning that they have been well-protected for centuries.
 Agronomical scenes in the Tomb of Nakht (circa 1400 –1390 B.C.); Metropolitan Museum of Art, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
Agronomical scenes in the Tomb of Nakht (circa 1400 –1390 B.C.); Metropolitan Museum of Art, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
Despite some paintings existing for over 4000 years, the colors accept remained extremely vibrant in the works that have been found and excavated. The purpose of these paintings was to create a pleasant afterlife for the deceased in their tombs, thus the themes traditionally seen in these artworks followed the concepts of the afterlife and protective deities. Some paintings even showed specific activities that the person enjoyed doing that they wished to carry on doing forever.
Egyptian paintings showed off the profile and side view of the individual or animal that was being captured.
This technique was called a composite view and was painted using specific bright colors, like ruby-red, black, blue, dark-green, and gold, which was then was mixed with egg whites so equally to stick to the surface. Another technique that was a distinctive characteristic of Egyptian paintings was that of a sunk relief, which was used in more prestigious tomb works. These reliefs were well-suited to bright sunlight every bit they could withstand the stiff sun without fading over time.
 KV9 Tomb of Ramses V-VI. Quaternary corridor, ornamentation on right wall: fifth section of the Book of Caverns (left side, the book continues off-frame to the right);R Prazeres, CC Past-SA iv.0, via Wikimedia Eatables
KV9 Tomb of Ramses V-VI. Quaternary corridor, ornamentation on right wall: fifth section of the Book of Caverns (left side, the book continues off-frame to the right);R Prazeres, CC Past-SA iv.0, via Wikimedia Eatables
The relief paintings found inside tombs were both high reliefs, where figures stood out from the wall, and low reliefs, where figures were actually carved into the wall. In society to create these types of paintings, the surface would be smoothed over and sanded. Artists would get-go create a miniature to refer back to before drawing filigree lines onto the wall and then as to replicate their work.
These paintings would first be outlined in cherry-red pigment, with corrections by other artists being done in blackness paint, before the final artwork was created.
Egyptian Drawings
One of the nigh well-known types of drawings to come out of ancient Arab republic of egypt was hieroglyphics. Existing as a form of pictorial writing and cartoon, hieroglyphics had an inherent sense of aesthetic dazzler. These symbols were typically used on ancient Egyptian monuments as a fashion to describe what the artwork meant. However, instead of acting equally a straight translation of what the object was, hieroglyphics stood for specific sounds and groups of sounds in club to explicate a work.
As they were seen as beautifully intricate, hieroglyphics are hands classified as another type of Egyptian drawings. Despite their simple course, hieroglyphics were an incredibly complex form of drawing and writing. Sentences could either start from the left or correct and be read from the top or lesser depending on how it would impact the elegance of the completed artwork.
 Ancient Egyptian hieroglyphs depicting the meeting notes of the fourth coming together of the 12;Camshea, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Eatables
Ancient Egyptian hieroglyphs depicting the meeting notes of the fourth coming together of the 12;Camshea, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Eatables
Due to the fact that Egyptian hieroglyphics were so confusing to read, an easy connection between the traditional alphabet and the hieroglyphic symbols could non exist made, as they encompassed two completely different languages. Over time, many historians take come upwards with a simplified translation of Western letters to hieroglyphics, so some sense and understanding can be fatigued from these artworks.
Thus, every fourth dimension a word was spelled out, these drawings would be used to convey the information to those reading the hieroglyphics.
Egyptian Sculpture
Most Egyptian sculpture was created during the early on dynastic period. Sculptures were typically carved equally both sunken and depression reliefs, as they adhered to the same conventions that governed Egyptian painting and were able to withstand the force of the sun. Figures who are not seated in sculptures were characteristically portrayed with parted legs, their heads in profile, and their torsos turned to directly confront individuals. This was considering they were made to direct face the rituals being conducted before them in tombs.
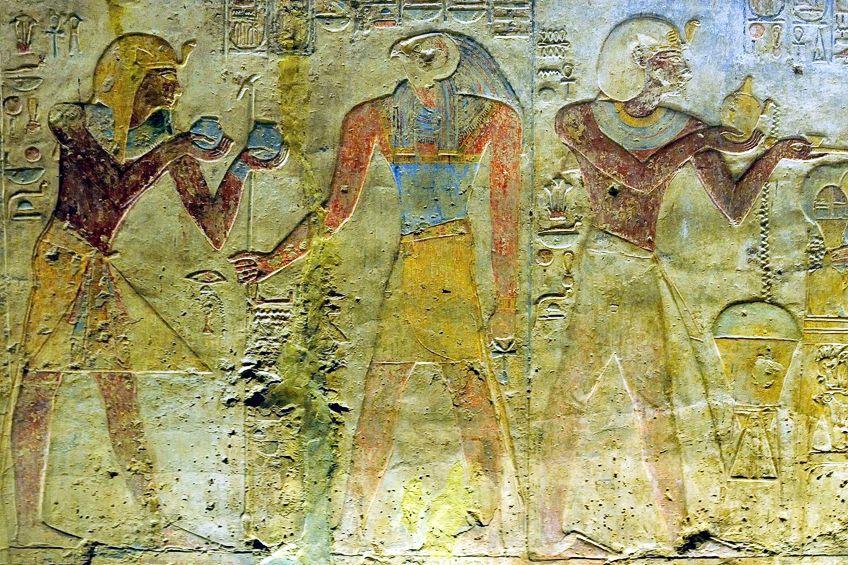 A relief of pharaoh Ramesses Two making an offering to Horus from the Temple of Beit el-Wali in Nubia;https://world wide web.flickr.com/photos/rivertay/, CC Past-SA 2.0, via Wikimedia Commons
A relief of pharaoh Ramesses Two making an offering to Horus from the Temple of Beit el-Wali in Nubia;https://world wide web.flickr.com/photos/rivertay/, CC Past-SA 2.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Strict rules were followed when crafting statues, every bit every god had rules for how their appearance was depicted. For example, the god of the heaven, Horus, was always depicted with a falcon's head no matter who carved him. Every bit all artists had to follow the aforementioned rules, their works were ranked according to their conformity with these features. Due to these rules inappreciably changing, the advent of Egyptian sculptures did not modify in over 3000 years. This was also intended to convey the permanence and non-crumbling qualities of the gods.
However, out of all the sculptures always made, the most iconic ones to come from ancient Arab republic of egypt were indeed the inexplicable Great Pyramids.
Standing on a natural rock shelf that is known as the Giza plateau today, these pyramids accept existed as burial places, memorials, and sites of worship for deceased rulers. Out of the pyramids that were synthetic, three are accounted to be the most important. The largest was made for Rex Khufu, the middle-sized one was made for his son, Khafre, and the smallest belonged to his grandson, Menkaure.
 Photograph of the famous Peachy Pyramids of Giza;Jan Caspar Philips (tekenaar) onbekend (graveur), Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Photograph of the famous Peachy Pyramids of Giza;Jan Caspar Philips (tekenaar) onbekend (graveur), Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Iconic Egyptian Artwork
Throughout history, many astounding Egyptian artworks take been unearthed in various temples and tombs. Due to the extensive archeological excavations that accept occurred in Arab republic of egypt throughout the decades, with these digs supposedly dating dorsum to the mid-1880s, very comprehensive collections of Egyptian artworks have been put together. Out of all these artifacts that accept been plant, the nearly iconic Egyptian artworks to ever exist remain the pyramids, with worldwide fascination surrounding these structures constantly growing.
The Great Pyramids of Giza
Classified as i of the seven wonders of the ancient world, the peachy pyramids of Giza are perhaps the well-nigh renowned and talked-about structures in history. For thousands of years, these gigantic monuments were unmatched in height, as individuals marveled over their unique and complicated construction, as they seemed almost too perfect to be real.
Enquiry has shown that the construction of the pyramids of Giza was the event of trial and error, with its success representing the pinnacle in the development of the purple mortuary complex.
Equally they were intended for the rulers of Egypt, they were built over the span of 3 generations for the pharaoh's Khufu, his son Khafre, and his grandson Menkaure. The proximity of these pyramids to i another was important, as beingness cached nigh the pharaoh was seen as an farthermost honor and supposedly ensured an esteemed place in the afterlife.
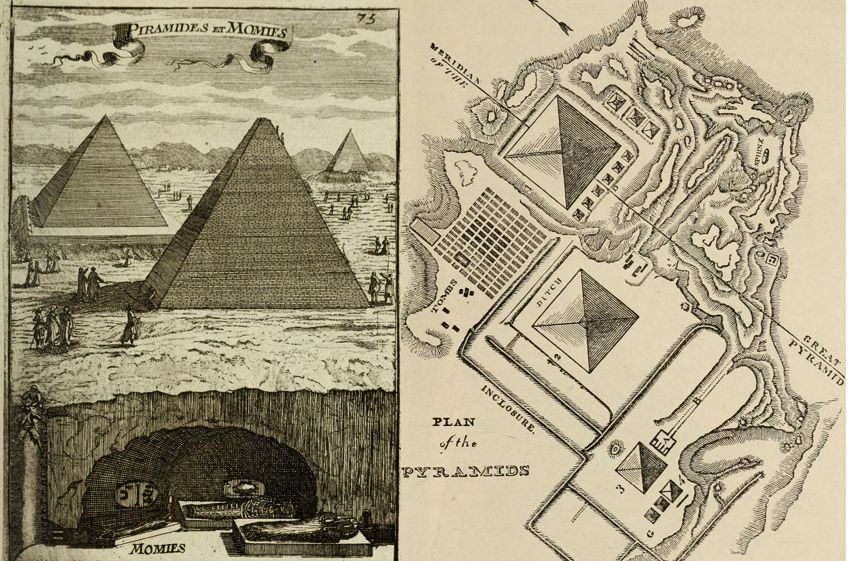
The Bang-up Pyramids of Giza. LEFT: Illustration fromDescription de l'univers (1683) depicting the Great Pyramids aboveground and one of the many tombs beneath; Cyberspace Annal Book Images, No restrictions, via Wikimedia Commons. RIGHT: A plan of the three Slap-up Pyramids of Giza, illustrating their proximity to one another, from the Handbook of Archeology (1867);Net Archive Book Images, No restrictions, via Wikimedia Commons
Throughout the decades, many questions take remained well-nigh the construction of these pyramids. The discovery of a town for workers to the south of the Giza plateau has provided some answers, as the individuals were thought to brand upwardly the permanent group of craftsmen and builders who worked on the pyramids. It has been estimated that roughly 20 000 workers helped build the pyramids, with about 340 small stones being moved daily from the quarry to the construction site during the 20 years it took to complete.
The shape of the pyramids of Giza was thought to exist a reference to the lord's day and the bending of its rays. The final betoken on top of the structure was seen equally a ramp for the pharaoh to mount into the sky. Despite their colossal size, the pyramids are unfortunately non permanent.
With the rapid growth that Cairo is experiencing, these structures will need increased consideration and safeguarding if they are to remain intact equally vital benchmarks of ancient Egyptian art.
Pyramid of Khufu
Also called the Great Pyramid, the largest of the Giza pyramids was intended for Pharaoh Khufu. With a height of 146 meters and a base length of more 230 meters per side, the pyramid of Khufu is regarded as an astounding engineering science achievement. What makes this pyramid so fascinating is its inner and outer casting stones, with an estimated 2 300 000 blocks of rock weighing upwards to l tons thought to accept been used.
Following his predecessors, the pyramid of Khufu was fabricated up of rough inner stones that were locally quarried and laid horizontally with spaces that were after filled with plaster. While originally built with outer casting stones, these accept since been advisedly removed, along with a capstone that used to sit down at the very top bespeak of the pyramid. Unfortunately, both the outer stones and the capstone would have made the pyramid visible from a greater distance if they were still there today, as they would have dazzled in the intense sunlight.
 Entrance to the Pyramid of Khufu, including a labeled diagram showing the interior chambers and passageways of the pyramid equally well as their dimensions;William Vaughn TupperFlickr uploader BPL, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Entrance to the Pyramid of Khufu, including a labeled diagram showing the interior chambers and passageways of the pyramid equally well as their dimensions;William Vaughn TupperFlickr uploader BPL, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
The interior passageways of the pyramid of Khufu add together to its uniqueness, as various puzzling features exist inside this structure. 1 of these features is an unfinished chamber whose role remains unknown, and several "air shafts" that fan out from the upper chambers. In recent times, these peculiarities have been explored through the use of small robots, just a series of blocking stones accept prevented further investigation into sure passages.
When inbound the pyramid, one has to climb upwards a narrow ascending bedroom that opens into the M Gallery.
In one case here, a passage leads into the King's Sleeping accommodation that was made entirely from red granite. Hither, Khufu's sarcophagus, which was sculpted from reddish granite, was found at the primal axis of the pyramid. Additionally, seven large brick-lined boat pits were located in the pyramid of Khufu, which were thought to transport the King to outstanding destinations in his afterlife.
Pyramid of Khafre
The 2d not bad pyramid, known as the pyramid of Khafre, was built by Pharaoh Khufu's second son, Khafre. Existing as quite a big structure, the pyramid of Khafre initially appeared larger than that of his begetter's but is in fact somewhat smaller. The reason for its gigantic appearance was that it was actually constructed about x meters higher on the Giza plateau than both of the other two dandy pyramids.
Due to this, the interior of the pyramid is much smaller and simpler than the pyramid of Khufu. Only a single burying chamber was congenital, along with one pocket-size secondary chamber and 2 passageways. Still, the place that the pyramid of Khafre appears to be more circuitous in design is in the mortuary temple at the base, as it exists as the more intricate structure when compared to the pyramid of Khufu.
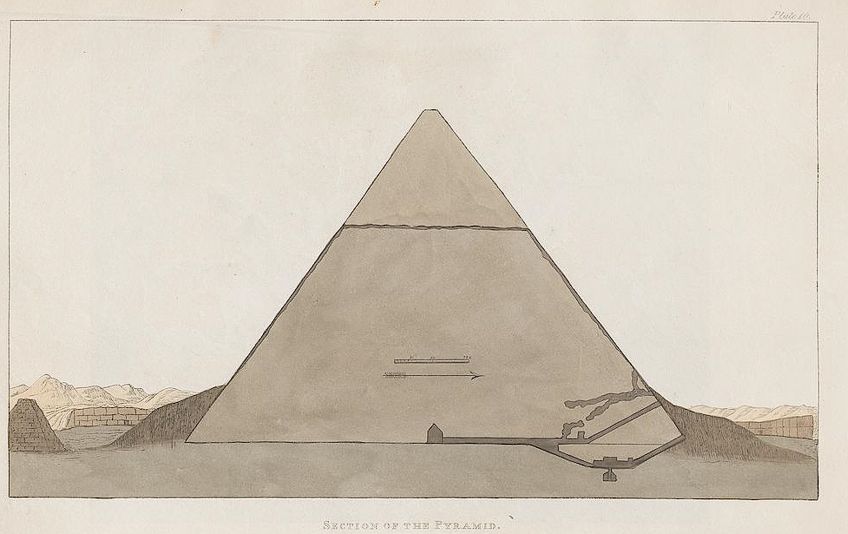 Cantankerous-Department of the Pyramid of Khafre;Agostiono Aglio, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Cantankerous-Department of the Pyramid of Khafre;Agostiono Aglio, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Inside the base, more than 52 statues of Khafre were constitute which filled the available space. These sculptures and images were either depicted as life-sized or larger, which represented the true prominence of the king. Upon excavation, statue bases indicated that an actress 24 images of the pharaoh were originally placed in this temple just were no longer there.
Due to its location at the east end, the pyramid'southward valley temple has been stunningly protected and maintained over time.
Pyramid of Menkaure
The 3rd pyramid that made upward the trio of the great pyramids of Giza belonged to Menkaure, the son of Khafre and the grandson of King Khufu. Equally it is the smallest of the iii structures, the peak of the pyramid only reaches 65 meters. Despite this, the pyramid of Menkaure has managed to preserve some of the most beautiful examples of sculpture to come from Egyptian history today.
The chambers of the pyramid of Menkaure are known to be more complex than the chambers in the pyramid of Khufu. This is because they include a chamber that was sculpted with decorative panels and another bedroom with six large alcoves. The burying chamber, which housed Menkaure'south embalmed torso was lined with gigantic granite blocks, with his sarcophagus existence carved with hollow panels as well.
 Tomb Chamber of Men-Ka-Ra! (1882), illustrated by Karl Werner (1881-1888);Fondo Antiguo de la Biblioteca de la Universidad de Sevilla from Sevilla, España, CC BY 2.0, via Wikimedia Eatables
Tomb Chamber of Men-Ka-Ra! (1882), illustrated by Karl Werner (1881-1888);Fondo Antiguo de la Biblioteca de la Universidad de Sevilla from Sevilla, España, CC BY 2.0, via Wikimedia Eatables
While Menkaure'southward pyramid was being excavated, it was discovered that neither his mortuary nor valley temples were always completed earlier he died. Within these chambers, a serial of statues of the male monarch were found, including a magnificent diad of him with his primary queen, Khamerernebty Ii, and various triads that depicted Menkaure beingness embraced past several deities.
The story of Menkaure's sarcophagus is an interesting one, equally it was considered to be an of import discovery when it was first found. However, while it was being transported back to England past gunkhole, the sarcophagus was lost at sea during a storm. This has led to Menkaure beingness considered as i of history's virtually important vanished treasures today. Additionally, the actual construction of the pyramid faced serious damage subsequently a flood at the cease of the vith dynasty and was almost entirely rebuilt.
The Bang-up Sphinx
Carved from the bedrock of the Giza plateau is the Great Sphinx, which is the 4500-year-sometime limestone statue that sits near the archway to the peachy pyramids leading from Khafre'southward valley temple into the mortuary. Measuring 20 meters loftier and 73 meters long, the Bully Sphinx exists every bit one of the world's largest and most iconic monuments, in improver to being one of the most identifiable relics constructed by the ancient Egyptians.
Within ancient history, a sphinx was a creature that had the trunk of a lion and the head of a human.
 A postcard depicting the Sphinx and the Pyramid of Cheops;B. Livadas & Coutsicos, CC BY-SA 2.5, via Wikimedia Commons
A postcard depicting the Sphinx and the Pyramid of Cheops;B. Livadas & Coutsicos, CC BY-SA 2.5, via Wikimedia Commons
Existing as a prominent figure in Egyptian, Asian, and Greek mythology, the Corking Sphinx is steeped in fable and folklore. In Egyptian history, a sphinx was thought to be a spiritual guardian and was more often than not portrayed as a male wearing a pharaoh headdress. Due to its proximity to Khafre'south pyramid and its slight resemblance to the pharaoh, the Swell Sphinx was said to have been carved specifically for the male monarch to offer protection.
Every bit the pyramid of Khafre was surrounded by the swell Sphinx and other statues, some scholars take stated that a angelic purpose explains the location of the Smashing Sphinx to Khafre's mortuary. As the king of beasts was a royal symbol that was connected to the sun, it has been suggested that the Great Sphinx was there to resurrect the soul of Khafre by channeling the power of the sunday and other gods. Despite existence but a theory, this provides a plausible caption for the structure's closeness to the pyramid.
![]() A photograph of the Sphinx in Cairo;New York Public Library, No restrictions, via Wikimedia Commons
A photograph of the Sphinx in Cairo;New York Public Library, No restrictions, via Wikimedia Commons
The Swell Sphinx exists equally one of the most interesting aboriginal Egyptian artworks, as so much is notwithstanding speculated about it.
It has been debated that the Sphinx is really far older than what is widely believed, based on the patterns of erosion nowadays on the structure. Additionally, as the word "sphinx" only originated in Greek mythology near 2000 years after the structure'due south completion, it remains unknown as to what the ancient Egyptian'due south called information technology.
Tutankhamun'due south Tomb
One of the nigh popular stories of ancient Egypt was the story of Tutankhamun condign pharaoh at the age of only nine years old. Discovered in 1922, the excavation of Tutankhamun's tomb in the Valley of the Kings is seen as ane of the most valuable archeological sites that have been found in Egypt. Yet, the story of Tutankhamun was almost completely lost to history as the archeologist, Howard Carter, who discovered his tomb ran out of fiscal backing and almost did non excavate at this site.
Upon discovery, the tomb was nearly intact and was habitation to a wealth of objects.
These finds take given historians and scholars an even closer and more unique insight into this specific period of the 18thursday dynasty of the New Kingdom when King Tutankhamun ruled. His fourth dimension ruling Egypt was rather circuitous and short-lived, as Tutankhamun married his half-sis Ankhesenamun, did not produce any heirs, and died at the young age of eighteen. Manners of his death accept been widely speculated and today, the answer remains a mystery still.
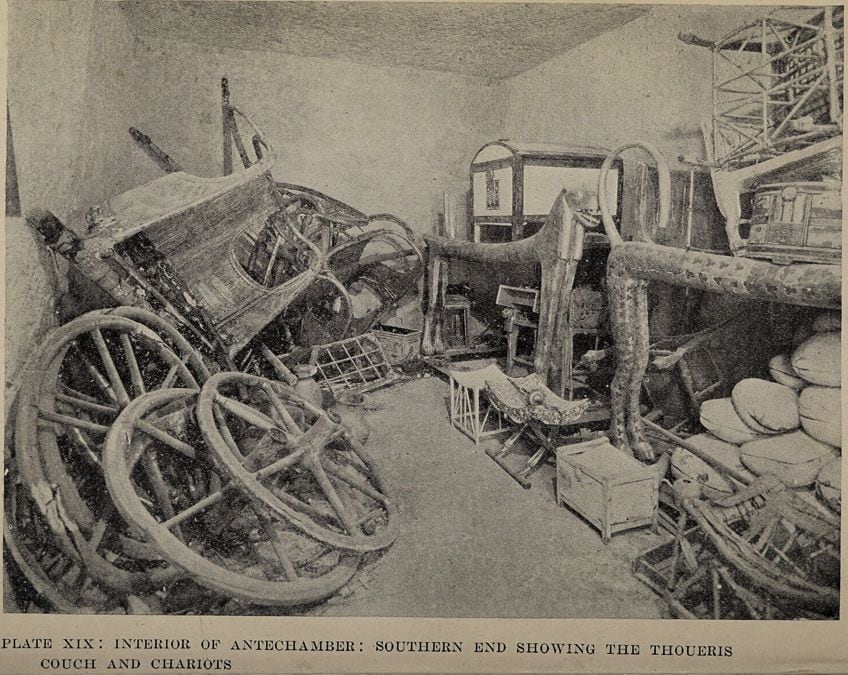 Analogy from the Tomb of Tut-Ankh-Amen, Plate 19, Interior of the Anteroom, Southern End Showing the Thoueris Couch and Chariots, past Howard Carter and A. C. Mace, illustrations and photographs by Harry Burton, 1923;Harry Burton (illustrator & photographer), Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Analogy from the Tomb of Tut-Ankh-Amen, Plate 19, Interior of the Anteroom, Southern End Showing the Thoueris Couch and Chariots, past Howard Carter and A. C. Mace, illustrations and photographs by Harry Burton, 1923;Harry Burton (illustrator & photographer), Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Tutankhamun'due south tomb was robbed and resealed twice later on it was initially completed, with these robberies apparently hurrying up the structure of the tomb. Due to this, the tomb was found to be densely packed with items in great disorder as it was minor in size, as the robberies forced workers to seal the construction about immediately. Said to take been entered ii more times later on his mummy was buried, rumors take circulated about the "Curse of the Pharaoh" that face intruders who attempt to violate the king'southward last resting identify.
It took eight years to fully empty Tutankhamun'southward tomb due to the sheer number of objects plant and Carter's meticulous recording process.
Within his sarcophagus, an innermost coffin was constitute, every bit iii coffins held the body of Tutankhamun. The outer two coffins were made from woods and coated in gold and semiprecious stones, including lapis lazuli and turquoise. The innermost coffin proved to be the most improvident and valuable, every bit it was bandage in solid gold.
When the bury was originally found, it was not the shiny gilded image that we know today. Carter wrote in his notes that the coffin appeared to exist covered in a thick blackness layer from the hands down to the ankles. This was an anointing liquid, which was poured over during the burying to preserve it. Perhaps the most iconic object institute within the tomb was the decease mask of Tutankhamun. Seen every bit one of the masterpieces of aboriginal Egyptian art, the mask originally rested on the shoulders of the mummy of Tutankhamun within the gold bury.
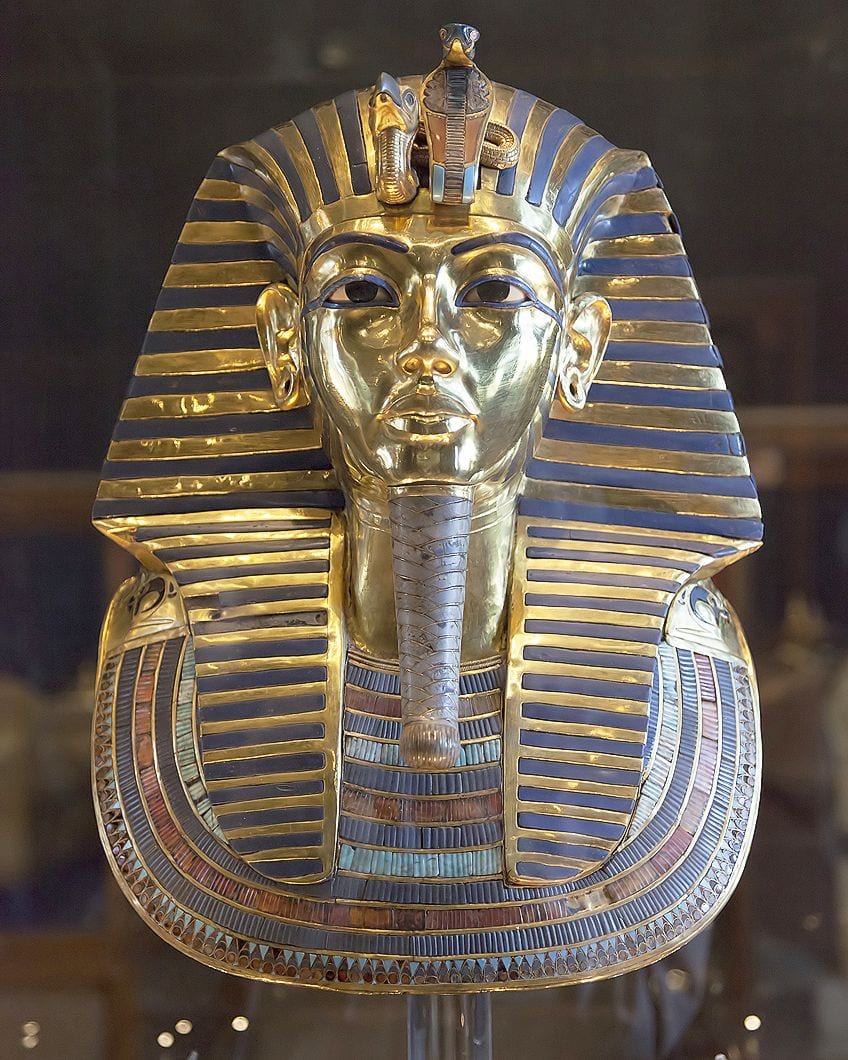 The Mask of Tutankhamun, c. 1327 BC. Made of gold, glass and semi-precious stones with a height of 54cm. It is currently being housed in the Egyptian Museum (Cairo);Roland Unger, CC By-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
The Mask of Tutankhamun, c. 1327 BC. Made of gold, glass and semi-precious stones with a height of 54cm. It is currently being housed in the Egyptian Museum (Cairo);Roland Unger, CC By-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
The mask portrays Tutankhamun to be wearing a striped cloth Nemes headdress, which was traditionally worn by pharaohs in ancient Arab republic of egypt, with the goddesses Nekhbet and Wadjet shown to be protecting his forehead. The fake beard that is seen was said to connect Tutankhamun to the image of a god, with the back of the mask being covered with Spell 151b from the Book of the Dead. This was used by ancient Egyptians as a guideline for the afterlife and was used to protect the torso of Tutankhamun equally he moved into the underworld.
Influence and Legacy of Egyptian Art
Ancient Egyptian art existed every bit an incredibly important period of art that went on to influence the European agreement, technique, and style which would exist observed for the adjacent 1000 years or so. The features and characteristics that are taken from Egyptian art only demonstrated a change in the late 19th and early twentyth century, when Italian artists formed the futurist group and began to split themselves from by ideals.
The beginning of modernistic art in society forced individuals to recognize the preconceptions that existed effectually fine art and so that a suspension from past styles and techniques could brainstorm.
This led to some Egyptian fine art coming under criticism as it was considered to be unpolished co-ordinate to new standards, despite being famously adored and respected for so many years prior. Some critics went as far as to say that Egyptians never truly learned the element of perspective, equally no interaction of calorie-free and shadow was seen in the artworks plant.
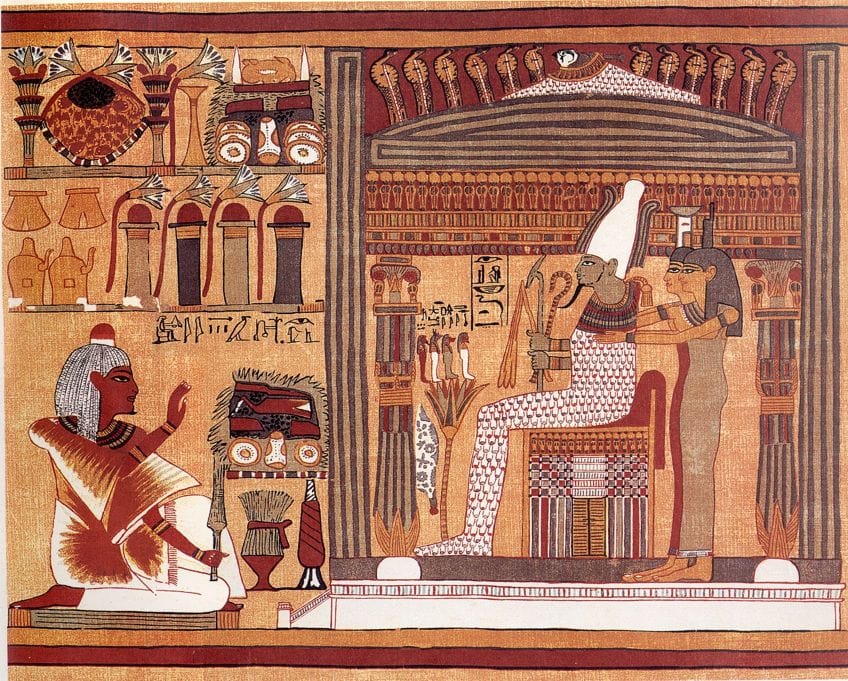 Facsimile of a vignette from the Volume of the Dead of Ani. The deceased Ani kneels earlier Osiris, judge of the dead. Behind Osiris stand his sisters Isis and Nephthys, and in front end of him is a lotus on which stand up the 4 sons of Horus. Scanned from The Egyptian Book of the Expressionless: The Book of Going Forth past Day past James Wasserman et al (1994), facsimile created 1890; original artwork created c. 1300 BC;British Museum, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Facsimile of a vignette from the Volume of the Dead of Ani. The deceased Ani kneels earlier Osiris, judge of the dead. Behind Osiris stand his sisters Isis and Nephthys, and in front end of him is a lotus on which stand up the 4 sons of Horus. Scanned from The Egyptian Book of the Expressionless: The Book of Going Forth past Day past James Wasserman et al (1994), facsimile created 1890; original artwork created c. 1300 BC;British Museum, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Additionally, other Egyptian artwork began to be targeted equally the world of fine art started to move in a completely new direction, every bit works were seen as 2-dimensional and emotionless. Fifty-fifty iconic statues that were previously praised, such as sculptures depicting battle scenes, kings, and queens, were labeled as impassive and cold and therefore not fitting for the new genre of art.
Yet, what these critiques failed to recognize was the functionality of Egyptian art. Artists understood the importance of emotions, but also knew that they were a temporary state. Thus, depicting statues and paintings with one single emotion would accept led to an inauthentic artwork being created equally individuals were non consistently happy or sad, and a false scene would residue in ane's tomb for all eternity. Due to this, Egyptian art demonstrated an elevated knowledge almost including the transient nature of emotion in artworks.
In essence, Egyptians saw life every bit only the smaller part of an eternal journey that all individuals would commence on, with Egyptian fine art accurately reflecting these beliefs. This led to artworks that were made to withstand the examination of time, allowing society today to look dorsum at and consider artworks that existed thousands of years ago. The influence of Egyptian art on the current creative society has proved to exist invaluable, as the values and beliefs of Egyptian artists take gone on to inform the basic premise of what art stands for today.
Take a expect at our ancient Egyptian art webstory here!
Oft Asked Questions Nigh Egyptian Art
What Is Egyptian Art?
Dating back to the pre-dynastic period, Egyptian art has developed for thousands of years within Arab republic of egypt. Initially, art was reserved for the wealthy elite and the pharaohs who ruled Egypt, meaning that only those who could afford artworks had access to them. Existing every bit an art form that primarily served a purpose, Egyptian art prioritized office over aesthetic beauty as art was made to help those who passed away forth the journey of inbound into their eternal afterlife.
What Were the Of import Characteristics of Egyptian Art?
As artworks were made for a specific objective, Egyptian artists generally made use of the same important characteristics within their works so as to accurately accomplish their desired goal. These characteristics included the utilization of anonymity, symmetry, and symbolism. If all of these elements were finer combined, artworks that were truly Egyptian in fashion were considered to be made.
What Are Some of the Most Famous Examples of Egyptian Art?
Some of the virtually iconic examples of Egyptian art are the sculptural figures and objects that were fabricated. These include the great pyramids of Giza, the pyramid of Khufu, the pyramid of Khafre, the pyramid of Menkaure, the Great Sphinx, and Tutankhamun's tomb.
Source: https://artincontext.org/egyptian-art/
0 Response to "The Art of Predynastic Egypt Is Principally Made of Quizlet"
Post a Comment