what factors appear to lead to bamas ability to compete with much larger competitors?
The Five Forces of Porter framework is a rather useful tool to decide the attractiveness of an industry. Named after Michael Due east. Porter, the Five Forces of Porter framework dictates that at that place are five forces that determine the overall competitive intensity and attractiveness of a marketplace. It is particularly helpful in evaluating whether or not a company should enter a particular manufacture. For that reason, it is very popular and widely used, for case to analyse the industry construction of a company or its corporate strategy.
Porter defines five forces which provide a articulate movie of the potential profitability of entering an industry. This is based on the concept that the v forces assist to determine the competitive intensity, which in turn mirrors the attractiveness of the industry. An unattractive manufacture is ane in which the overall effect of the forces reduces profitability. The most unattractive manufacture would exist an industry with pure contest.
The framework can exist applied to whatsoever segment of the economy to assess potential profitability and full general attractiveness. In fact, the framework provides an explanation why different industries are able to sustain different levels of profitability.
The Five Forces in the Five Forces of Porter Framework
The Five Forces of Porter Framework analyses five factors that shape every industry. After having investigated each of these factors, you should have a articulate moving-picture show of the opportunities and threats provided past the industry.
- Competitive Rivalry
- Bargaining Power of Customers (Buyer Ability)
- Bargaining Power of Suppliers (Supplier Power)
- Threat of New Entrants
- Threat of Substitutes
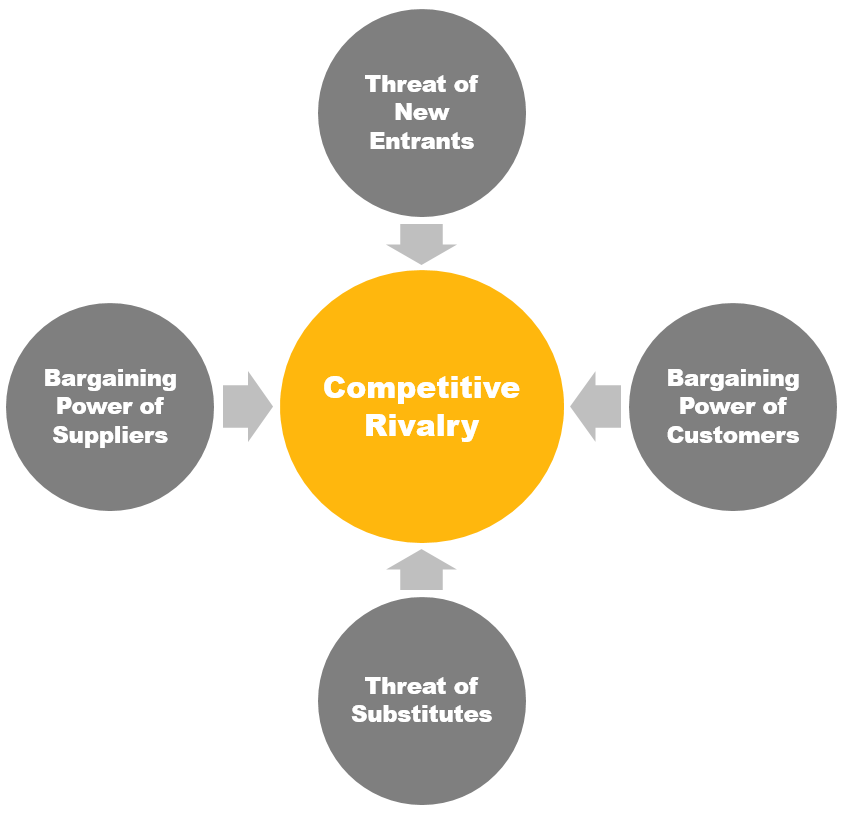
Five Forces of Porter Framework – Assessing the Attractiveness of an Industry
Competitive Rivalry
The most fundamental gene in the Five Forces of Porter Framework is competitive rivalry. The reason for this is that all other factors impact competitive rivalry. And so what do marketers need to consider?
Competitive rivalry is determined primarily by the post-obit factors:
- Number and size of competitors (industry concentration)
- Competitor strategy
- Competitor resources (e.thousand. for advertisement activities or new product development)
- Industry growth
- Go out barriers
- Share of fixed costs
- Differentiation (e.grand. differences in prices, quality, etc.)
Threat of New Entrants
Clearly, there is a direct link betwixt an bonny industry and the threat of new entrants: If an industry is perceived equally bonny, new entrants are likely to announced. A larger number of competitors in turn volition lead to lower profitability across the industry, which in turn may lower the attractiveness over again.
Of import criteria that influence the threat of new entrants incorporate:
- Upper-case letter requirements
- Entry barriers (rights, patents, technology protection etc.)
- Access to inputs
- Learning curve
- Economies of scale
- Customer loyalty
- Government policies (to either encourage or discourage new entrants)
Threat of Substitutes
If customers tin hands substitute your product or service for another, the threat of substitutes is high. This is not the same as switching to a different company with the aforementioned offering, but switching products entirely. For example, Pepsi is not a substitute to Coca Cola, but for somebody seeking primarily a caffeinated drink, coffee or green tea may be a substitute. The more products fulfilling the aforementioned need there are, the higher the chances your customers volition be drawn to a substitute. How to confront this?
- Number of substitute products
- Perceived level of differentiation
- Switching costs (a cost to the buyer for switching to the culling)
- Attractiveness of substitutes to buyers
- Price-performance trade-off of substitutes
Bargaining Ability of Suppliers
Every company has suppliers, whether for raw materials, knowledge back up or whatever else. Often, a lot of inquiry and consultation is necessary to reach the best suppliers at the best price. For some companies, the pick of supplier has a significant impact on the business organization upshot, due to specialist knowledge, technology, quality, or only prices. For others, just virtually any of the available suppliers may practise the job. But what if there is very little option of suppliers? The fewer suppliers fulfilling the company's requirements at that place are, the more power they have over the company and the prices they tin can accuse. Marketers should consider:
- Number of available suppliers (fulfilling the company's requirements)
- Size of suppliers
- Switching cost (costs to both the company and the supplier for switching)
- Differentiation of inputs
- Impact of inputs on price or differentiation
Bargaining Ability of Customers
Too the customers can have power over the company. This is the case whenever they tin exert pressure to companies, in particular force per unit area to lower their prices. If buyers have a large selection of products and companies to choose from, the power they accept over the visitor is loftier as they can hands decide to switch the company. Equally, if the company depends on just a few large buyers, they have an extreme ability over the company as one of them leaving may mean problem for the company. The bargaining power of customers is determined by:
- Number of buyers and importance of one individual heir-apparent for the company
- Toll sensitivity
- Buyer book
- Buyer information (what data about the market practise customers have, and how much data is available to yous on your buyers?)
- Differentiation of the company and its products
The table beneath summarizes key determinant factors for each of the v forces in the Five Forces of Porter Framework.
| Competitive Rivalry | |
| · Number and size of competitors (industry concentration) · Industry growth · Get out barriers · Share of fixed costs · Differentiation | |
| Bargaining Power of Suppliers | Bargaining Ability of Customers |
| · Supplier concentration · Switching cost · Differentiation of inputs · Impact of inputs on toll or differentiation · Presence of substitute inputs | · Bargaining leverage · Heir-apparent volume · Buyer information · Price sensitivity · Production differentiation |
| Threat of New Entrants | Threat of Substitutes |
| · Entry barriers · Access to inputs · Learning curve · Economies of scale · Upper-case letter requirements | · Switching costs · Attractiveness of substitutes to buyers · Price-performance trade-off of substitutes |
Source: https://marketing-insider.eu/five-forces-of-porter-framework/
0 Response to "what factors appear to lead to bamas ability to compete with much larger competitors?"
Post a Comment